Wildfire smoke plumes
Long range transport of wildfire smoke aerosols
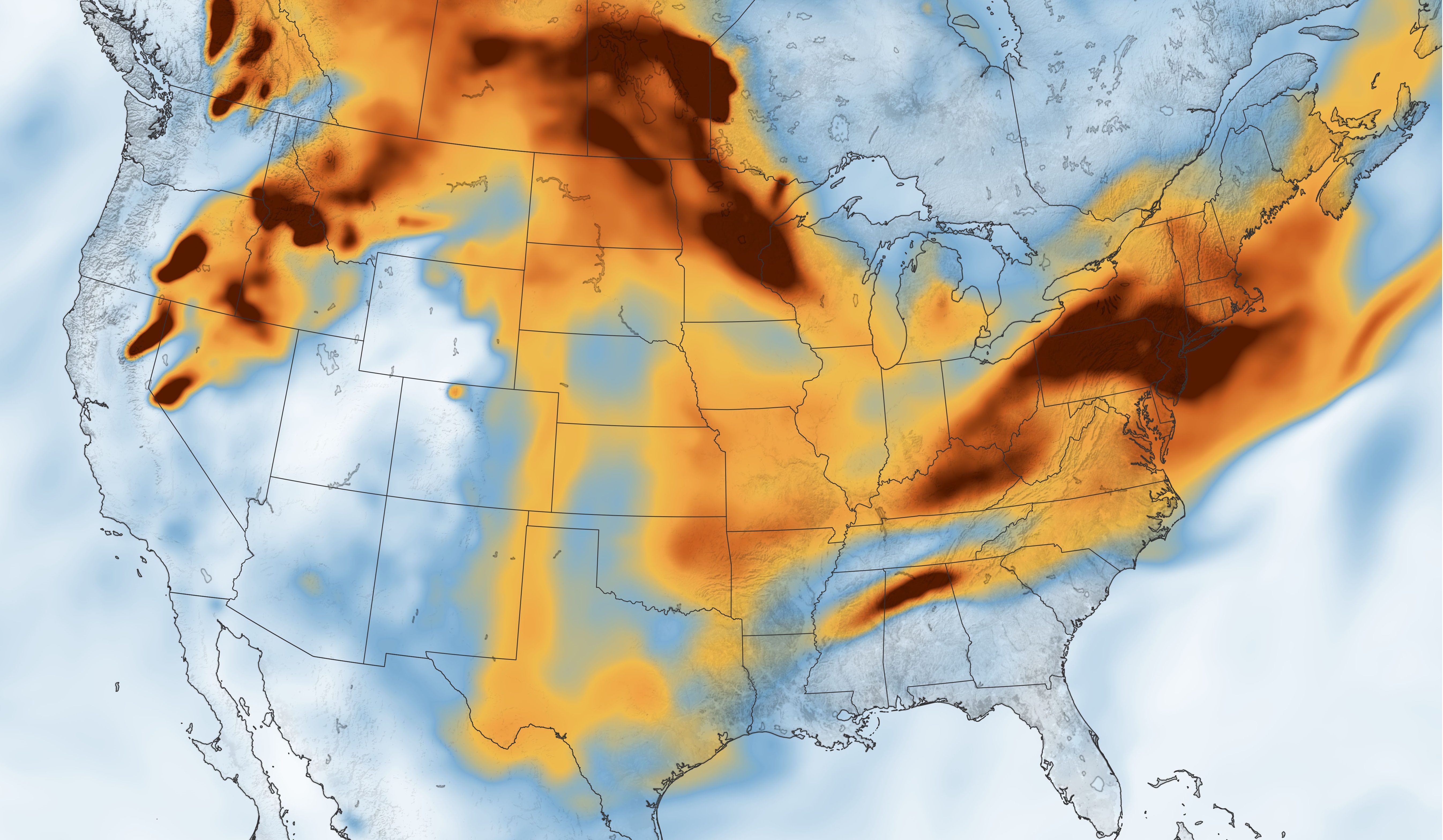
Wildfire smoke (July 21, 2021) simulated by NASA GEOS forward processing (GEOS-FP)
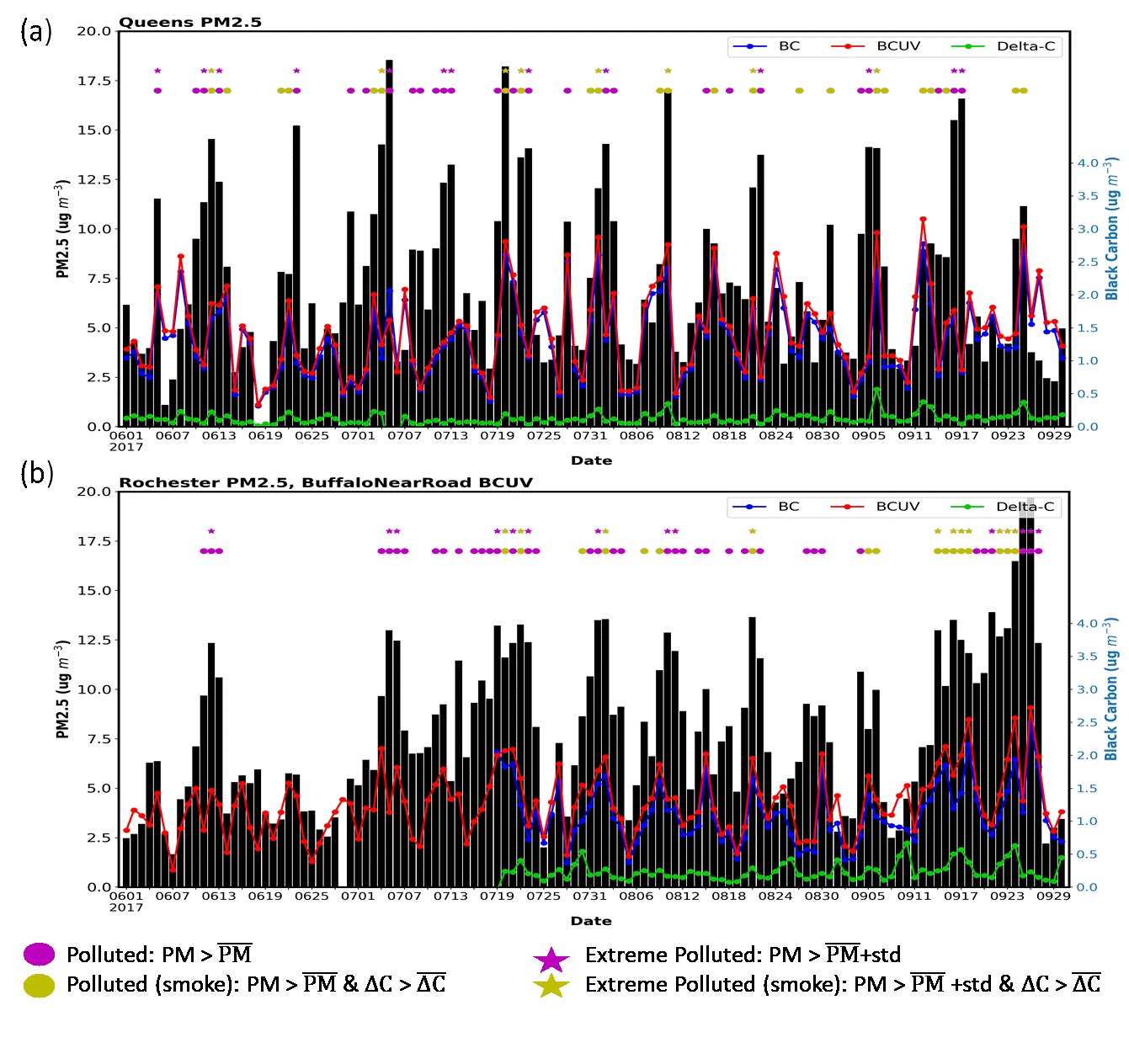
Long-range transport of smoke aerosols and their impacts on local air quality over NYS were investigated using satellite measurements, ground-based networks, and model products. Machine learning algorithms were applied to characterize key contributors to surface PM concentrations.
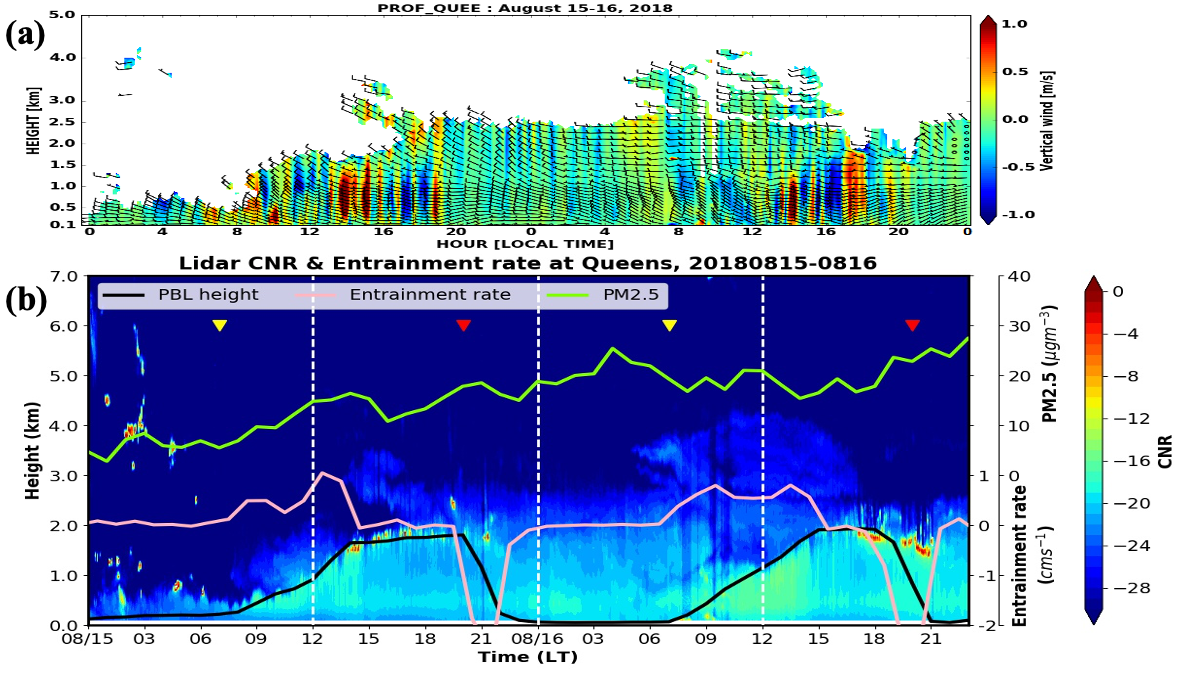
Aloft smoke plumes
Wildfire smoke aerosols, once emitted, can transport over long distances and affect surface air quality in downwind regions. Hung et al. (2020) and Lin et al. (2021) investigated the intra-continental smoke transport and its impact on NY air quality. The group continues the efforts to investigate the processes for mixing aloft smoke aerosols down to the surface.
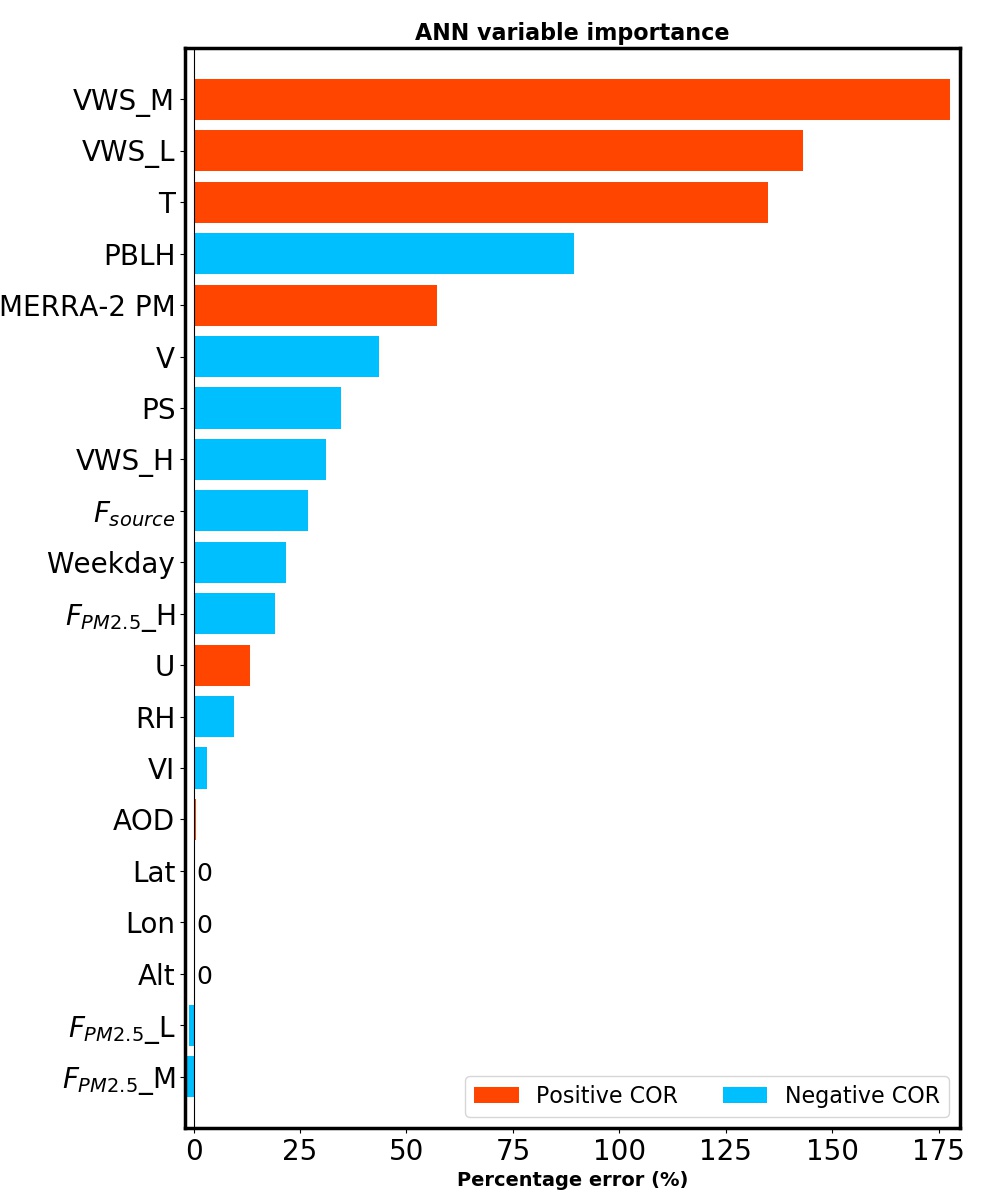
Applying machine learning
Machine learning techniques were used to estimate surface PM2.5 mass concentration from various predictors in Hung et al. (2020). Application of vertical and source predictors generally improves model performance, shown in Hung et al. (2021).